A reciprocating compressor or piston compressor is a positive-displacement compressor that uses pistons driven by a crankshaft to deliver gases at high pressure. The heat exchangers that are used in a normal piston compressor are removed as the heat is removed in the cylinder itself where it is generated Reciprocating Compressors.
Reciprocating air compressors work on the principle of reciprocation, which means to move something back and forth. Also known as piston compressors, these machines are positive displacement equipment, meaning that they increase pressure in air to compress it.
Reciprocating compressors have many uses in industry, including natural gas processing and delivery, chemical plants, and oil refineries. Compressed gases also play a major role in refrigeration technology, where the subsequent re-expansion of the gas after compression produces the required cooling effect.
A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor. Compressors are similar to pumps: both increase the pressure on a fluid and both can transport the fluid through a pipe.
The three most common air compressors are the reciprocating, rotary screw and centrifugal. Reciprocating air compressors are considered positive displacement machines, which means they increase the pressure of the air by reducing its volume.
Capacity Flow Rate 3 -40 CFM (@10 bar Pressure)
Motor Rating: 1 - 15 HP (0.75-11 kW)
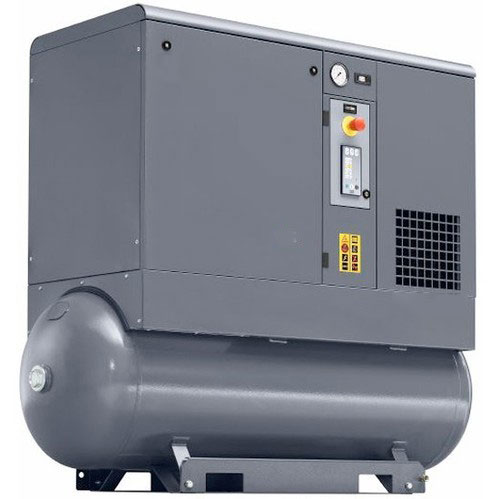
Tank mounted – Tank mounted rotary screw air compressors are rotary screw compressor systems that are mounted to an air receiver tank. The receiver tank stores compressed air for instances where the amount of compressed air required rises. Rotary screw air compressors operate by trapping air between two meshed rotors and reducing the volume of that trapped air as it moves down through the rotors. This reduction in volume results in compressed air, which can then be used to power air tools, inflate tires, or in numerous other applications. The basic principle of a screw compressor is as the male and female rotors are rotating in opposite direction they draw air in between them. As the air progresses along the rotors the air is compressed as the volume space between the rotors decreases, hence creating compressed air that is displace to the outlet.
The three most common air compressors are the reciprocating, rotary screw and centrifugal. Reciprocating air compressors are considered positive displacement machines, which means they increase the pressure of the air by reducing its volume.
The two main types of compressors are dynamic and positive displacement. The positive displacement compressor is probably the one you're familiar with. It traps gas in a volume and then decreases that volume. The decrease in volume causes a rise in pressure
There are two basic types of dynamic compressors and these are:
Centrifugal compressors.
Axial compressors.
Generally, screw air compressors replace piston compressors when a large volume of high-pressure air is needed. This can be to operate large commercial and industrial applications or high-power air tools.
Capacity Flow Rate 10-70 CFM (@10 Bar Pressure)
Motor Rating: 3-20 HP (2-15 KW)

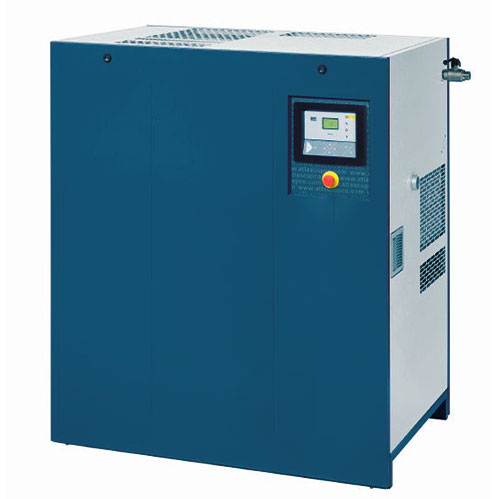
One common supply side technology is the variable frequency drive (VFD) of the compressor. It is well-documented that positive-displacement compressors with VFDs provide cost-effective savings in comparison to inlet modulating, load-unload, and variable displacement control. Variable frequency drives (VFDs) are being used in the HVAC industry more frequently and in more applications. They can modulate the motor speed very smoothly within a wide range. Reduced motor speed provides a significant reduction in motor power. The three most common air compressors are the reciprocating, rotary screw and centrifugal. Reciprocating air compressors are considered positive displacement machines, which means they increase the pressure of the air by reducing its volume.
Variable speed compressors work by using an inverter to speed up or slow down the motor according to heating or cooling load. Instead of all the power going directly into a traditional AC compressor (which runs at a fixed speed), the inverter provides the compressor with a specific voltage, essentially saving energy Output voltages are available for VFDs to match almost any existing motor voltage. However, very few, if any, VFDs have a direct 13,800-volt output for very high-voltage motors. For these cases, using a step-up transformer on the output of the VFD is often necessary to match the motor voltage
The six factors you should be considering when choosing a VFD.
1. Full Load Amperage. The first step in this process is making sure the drive can handle the motors current demands. ...
2. Overload. ...
3. Application Type. ...
4. Altitude. ...
5. Temperature. ...
6. Carrier Frequency.
Capacity Flow Rate 10-70 CFM (@10 bar Pressure)
Motor Rating: 3-20 HP (2-15 KW)
